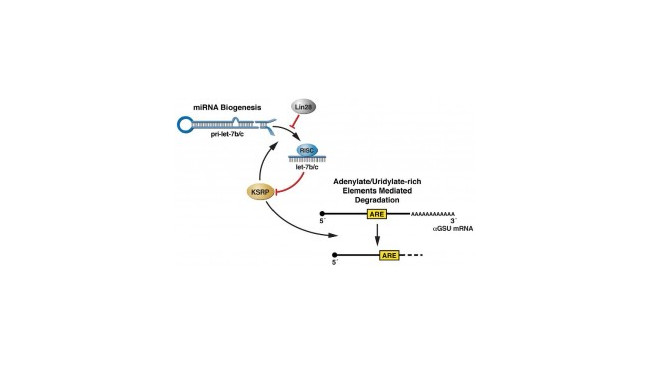
Investigation of novel mechanisms of miRNA-dependent gene expression control
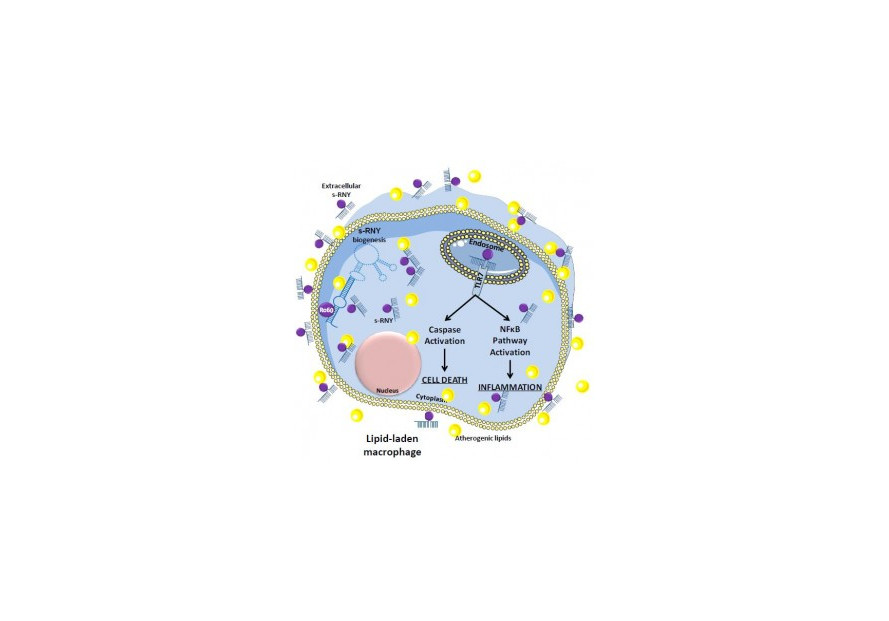
A model for s-RNY mode of action in lipid-laden macrophages exerting signaling pathway effects
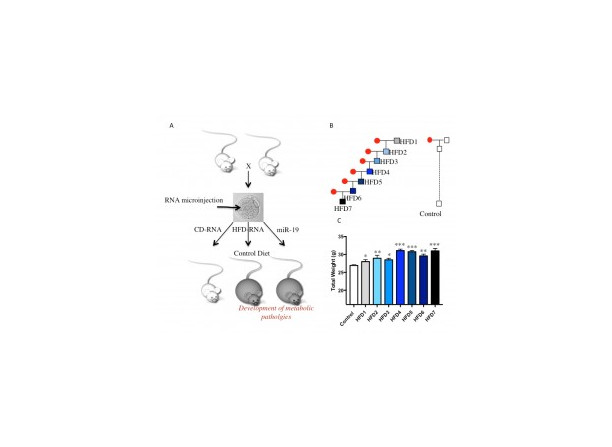
Role of small RNAs in epigenetic inheritance of metabolic pathologies
Bioinformatics tools development to study the protein/miRNA code to orchestrate the post- transcriptional programme(s) of regulated gene expression.
In the past few years a series of paradigm-shifting discoveries have radically altered our understanding of mechanisms underlying integrated gene expression programmes, including the widespread transcription of non-coding RNAs. In particular, the discovery of the regulatory small RNAs represents a major breakthrough in recent biomedical history. In our current research, we are investigating the molecular mechanisms responsible for orchestrating and integrating genome-wide transcriptional and post-transcriptional responses upon changes in extracellular cues critical for diverse biological processes, including developmental, physiological, and pathological events. We focus on previously unsuspected non-coding RNA-mediated strategies in regulating gene expression. These strategies, which underlie genome-wide transcriptional and post-transcriptional responses, are controlled by complex networks of protein/RNA interactions, ~50 percent of which are expected to be cell-type specific. Despite their discovery more than 35 years ago, the fundamental principles by which non-coding RNAs are regulated and functional have been poorly understood. Our recent findings have contributed to unravel novel and unexpected biological and biochemical aspects of such a central role of noncoding RNAs in regulated gene expression programmes. Our works also extended the knowledge of non-coding RNAs toward novel therapeutic and diagnostic implications for many common diseases, including atherosclerosis, diabetes, and cancer. Presently, many questions about RNA biology in gene expression control are still to be fully addressed, including i) how do fate of RNAs ultimately influence their function? ii) what are the biochemical mechanisms underlying the function of noncoding (nc)RNAs? A major challenge for both questions will be to define the components of the ribonucleoprotein complexes that ultimately determine the fate and function of ncRNAs in timing and cell specific fashion. Overall, we foresee that in vivo experiments and OMICS approaches coupled with proteomic and transcriptomic methodologies will be the most exhaustive path to uncover the role of ncRNAs in physio-pathological events of gene expression. experimental methodologies and OMICS



